Theme:
Polymer Chemistry 2020
About Conference:
On this prestigious event, we heartily invites all the eminent personalities, researchers, scientists, students and delegates from all over the world to attend “4th World Congress on Polymer Chemistry” during October 26-27, 2020 in Vienna, Austria. The conference is mainly focused on the theme of “Exploring and Novel innovations in Biopolymers and Polymer Chemistry” aims to blooming up the new research innovations, concepts and technologies in Polymer Science.
Conference Theme: "Exploring and Novel Innovations in Biopolymers and Polymer Chemistry"
The distinctive plan behind the conference is to give an opportunity for leading academicians, scientists, researchers and industrial professionals from around the globe to gather and have discussion on the most recent advancements within the interlinked domains of science, business and technology and its research benefits for each other domains progress.
Young Scientist Benefits:
- Our conferences give best Platform for your research through oral presentations.
- Share the ideas with each eminent researchers and mentors.
- Young Scientist Award reorganization certificate and memento to the winners
- Young Scientists can get acceptable and timely information by this Forum.
- Platform for collaboration among young researchers for good development
- Award should encourage participants to strive to realize their full potential which could in turn be beneficial to the field as whole.
Deadline for Registrations:
Platform for collaboration among young researchers for better development
- Till May 25, 2020 – $399
- Till June 25, 2020 – $499
- Till July 25, 2020 - $599
Why to attend:
Polymer Chemistry Congress that goes to be the leading conference and provides a foremost technical forum for sharing, learning the analysis & advancements in conjunction with conversing new thoughts and technologies. Polymer Chemistry 2020 has sessions on recent developments in Biopolymers and Polymer Chemistry. This can be comprised of symposiums, Workshops, B2B Meetings Etc. It is a great opportunity for advertisers and Sponsors.
Target Audients:
Eminent Professionals of Biopolymers and Polymer Science, Chemical Engineering Researcher professors, Junior, senior research fellows, Directors of Polymer related companies, Students, Members of different Physics and Chemistry associations and etc.
Track 1: Biopolymers and Biomaterials
Biopolymers are Polymers that are made by living organisms. Biopolymers contain monomeric units that are covalently secure to create larger structures. Biopolymers and Biomaterials include materials from proteins, DNA and carbohydrates to artificial or natural materials that are built to act with biological systems for medical functions.
There are three main categories of biopolymers, classified in keeping with the monomeric units used the structure of the biopolymers formed-
- Polynucleotides (RNA & DNA) – long polymers composed of 13 or more nucleotide monomers.
- Polypeptides – short polymers (amino acids)
- Polysaccharides –linear bonded polymeric carbohydrate structures
Track 2: Recycling and waste management of Biopolymers
Bio-plastics are created exploitation renewable feed stocks instead of being derived directly from oil. Bio-plastics can be used in the production of conventional polymers that can be recycled, such as recycled PET (Polyethylene terephthalate) or biodegradable polymers such as PLA (Polylactic acid). Increasing the volumes of synthetic polymers is manufactured for various applications. Plastic use refers to a way that retrieves the first plastic material. However there are several refined strategies accessible for the treatment & management of waste plastics.
A polymer waste requires complimentary combinations of -
- Biodegradation
- Incineration
- Recycling
- Chemical and mechanical recycling
Track 3: Future Scope of Biopolymers and Polymers
Future of Biopolymers and Polymers demand the manufacture for brand spanking new materials is overwhelming. In search of novel advanced materials solutions and keeping an eye on the goal of property production and consumption, bioplastics have many potential benefits. The main concerns for humans in the future can be energy and resources, food, health, mobility & infrastructure and communication. Polymers occupy an outstanding role during this modern living. The use of renewable resources to produce bio based materials is the key for increasing resource efficiency. The resources will be cultivated on an annual basis, the principle of cascade use, as biomass will be first used for materials and so energy generation, a reduction of the carbon footprint and saving fossil resources.
- Biopolymers in Stem-Cell technology
- Ceramics and Applications
- Biopolymers in drug delivery
- Biopolymers in marine sources
- Market growth of biopolymers
Track 4: 3D Printing Polymers
The term 3D printing originally stated a method that deposits a binder material onto a powder bed with inkjet printer heads layer by layer. More recently, the popular vernacular has started victimization the term to cover a wider type of additive manufacturing techniques like electron beam additive producing and selective optical device melting. The most commonly used 3D printing method is a material extrusion technique referred as “fused deposition modelling”.
There are many different 3D printing processes-
- Vat Photo-polymerization
- Material Jetting
- Powder bed fusion
- Directed energy deposition
- Sheet lamination
Track 5: Applications of Biopolymers and Polymer Chemistry
Biopolymers are polymers made by living organisms. Biopolymers contain monomeric units that are covalently bonded from larger structures. Cellulose is the most commonly occurring organic compound and biopolymer on earth. The term Polymer refers to a molecule whose structure consists of multiple continuance units, from that originates a characteristic of high relative molecular mass and attendant properties. Polymers have properties that build them appropriate to be used in protective product from wetness, increasing shelf-life and creating product easier to dispense. Each Biopolymer has its own material specific properties.
- Biopolymers for food packaging
- Advances in biopolymer productions
- Renewable biomass Sources
- Biopolymers in molecular recognition
- Polymers in electronics
Track 6: Polymer Nanotechnology
Polymer nanocomposites include a polymer or copolymer having Nano particles dispersed with in the polymer matrix. Nanotechnology has created important contributions to the formulation of adhesives, sealants, coatings, potting and encapsulation compounds. The transition from micro to nanoparticles results in modification of its physical and chemical properties. The two key factors during this are the increase in the ratio of the surface area to volume and size of the particles. The increase in surface area to volume ratio that will increase because the particles get smaller ends up in associate increasing dominance of the behaviour of atoms on the area of particle overt that of these interior of the particle. This affects the properties of the particles when they are reacting with other particles.
- Nano-polymers in Nanomedicine
- Applications of Nanomaterials
- Nanopolymers and Nanotechnology
- Polymer Nanostructures
Track 7: Polymer Physics and its Characteristics
Polymer Physics is the study of mechanical properties and kinetic reaction of the polymer. Polymer is a very large molecule and it is very tough to analysis the characteristics of polymer. But with the assistance of statistical mechanical approach we will understand the property and the process of making polymer. And it also deals with the polymer, their fluctuations, mechanical properties, polymer structures. Basic phenomena are of interest in accordance with the applications of polymers in technologies such as optoelectronics, advance photovoltaic systems, coatings, composites, medicine, food and pharmacy, tissue engineering.
Characteristics:
- Low density
- Low coefficient of friction
- Poor tensile strength low mechanical properties
- Poor temperature resistance
- Good mould ability
Track 8: Biopolymers in Tissue Engineering
Biopolymers are widely used as biomaterials for the fabrication of medical device and tissue engineering scaffolds. Polymer scaffolds are drawing a good attention due to their unique properties like high surface to volume ratio, high porosity with very small pore size, biodegradation and mechanical property. They offer distinct advantages of biocompatibility, versatility of chemistry and also the biological properties which are significant in the application of tissue engineering and organ substitution. Tissue engineering is the immense area of research in recent years because of its vast potential in the repair or replacement of impaired tissues and organs. This analysis can target scaffolds as they are one in every of three most significant factors, as well as seed cells, growth hormones and scaffolds in tissue engineering.
- Tissue engineering in regenerative medicine
- Bone and cartilage tissue engineering
- Nano delivery systems
- Biopolymer methods in cancer therapy
Track 9: Synthetic and Natural Polymers
There are two types of polymers; those are synthetic and natural polymers. Synthetic polymers are derived from the fossil fuel oil, and are made by scientists and engineers. Natural polymers occur in nature and might be extracted. They are typically water based. Natural polymers as made naturally they will be easily degradable and may be consumed by the atmosphere. Most of the synthetic polymers are hard to degrade naturally and take long time in natural degradation.
- Synthetic Polymers: Nylon, Polyethylene, Teflon, Polyester and epoxy.
- Natural Polymers: Silk, Wool, DNA, Cellulose and Proteins.
Track 10: Polymer -Optics, Fibre and Lasers
Polymers are increasingly being used in a wide variety of applications in electronics and photonics, most of that use polymers in their ancient role as engineering materials. For quite 50 years we have been developing and producing polymer optical components and complex optomechanical electronic systems for our customers using sophisticated injection molding process. Metal nanoparticles are used since the medieval times to form stunning colours in glass windows.
Track 11: Organics Polymers
Organic polymers are macromolecules composed of many repeating monomer units. Both synthetic and natural polymer plays an important role in everyday life. Polysaccharides, polypeptides and polynucleotides are the main types of biopolymers in living cells. Polymers depending on their physical properties are characterised as thermoplastics, thermo sets, elastomers and fibers. Organic polymers are materials that essentially contain carbon atoms in the backbone.
Track 12: Biopolymers from Renewable Sources
Biopolymers from renewable resources are a completion of information on the diverse and useful polymers derived from agricultural, animal and microbial sources. Now a day it is clearly discovers from the present state of environmental preservation a nonstop definition and approval of growingly restrictive laws and a rise within the market demand for products with a lower ecological footprint. Particularly the auto mobile sector has been identified as one of the most involved in the adoption of protectionist measures towards the environment preservation, translating some of their major concerns in the increase of green materials demands.
Track 13: Bio-plastics and Bioinformatics
Bio-plastics are plastic materials made from renewable biomass sources like vegetable fats and oils, corn starch, straw, woodchips, sawdust, recycled food waste. Bio-plastic can be made from agricultural by-products and also from used plastic bottles and other containers using micro-organisms. Bioinformatics is a field of study that uses computation to extract information from biological data. It also includes the collection, storage, retrieval, manipulation and modelling of data for analysis, visualization or prediction through the development of algorithms and software.
Types of Bio-plastics:
- Starch based plastics
- Cellulose based
- Protein based
- Aliphatic polyesters
Track 14: Recent advancements in Biopolymers and Polymer Chemistry
Plastic packaging for food and non-food applications is non-biodegradable and additionally uses up valuable and scarce non-renewable resources like crude oil. With the present focus on exploring alternatives to petroleum and stress on reduced environmental impact, research in increasingly being directed at development of biodegradable food packaging from biopolymer based materials. Polymer Chemistry is the branch of chemistry which deals with large molecules made up of repeating units referred to as monomers. Polymer Chemistry includes branches which mimic the divisions of the field of chemistry as a whole with synthetic, physical, biological and analytical chemistry.
Polymers and Plastics are some of the most important and most generally used chemical product in trade and shopper markets. They are used for producing consumer products like coatings, lubricants, consumer goods, aerospace, building materials etc. The global polymer market is obtaining majorly disrupted by biopolymers-one amongst the world’s most organic compounds. The categorization of biopolymers is basically dependent on its end user industry. This market enjoys a varied range of end users as well as some promising ones like pharmaceutical, healthcare, food and drinkable business. In the medical industry, biodegradable polyesters are extremely useful in manufacturing surgical implants.
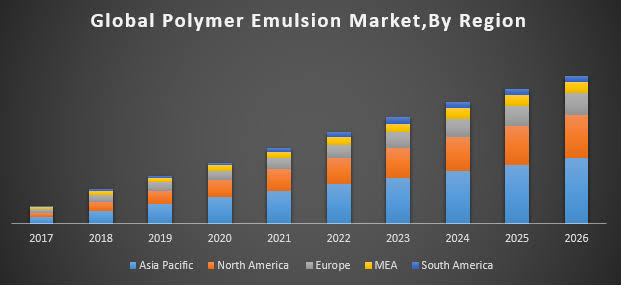
In the year 2018, the global biopolymers market experienced noticeable growth that is why its evaluated size was at $12 billion. The bio-polymers market is projected to register a CAGR of 22.68%, throughout the forecast period (2019-2024).
Key market trends: Food and beverages industry is expected to witness a significant growth in the forecast period; Asia-Pacific is expected to register a fastest growth rate in the forecast period; Competitive landscape.
Previous Conference Report – Polymer Chemistry 2020
Another Polymer Science and Engineering has been effectively executed- The 3rd edition – and we need to thank the attendees Conference Centre Staff, and the Organizing Committee, Ad-Sponsors & Media partners and anyone else that helped to make this “3rd International Conference on Polymer Science and Engineering with the theme- Journey from innovations to applications of new generation technologies a successful conference”.
To attendees-We hope that you acquired the sort of develop technical records in the arena of Polymer Science and Engineering and Biopolymers and Bioplastics two that you have been seeking, and that your role in the discipline has been more suitable by your participation. We hope that you have been in a position to take part in all the sessions and take advantage of the extremely good advancements in Polymer Science and Engineering & Biopolymers two and Bioplastics that scientists are working with.
The meeting covered various sessions, in which the discussions included the scientific tracks:
- Polymer Science – The Next Generation
- Polymers and the Future of Industries
- Polymer Nanotechnology
- Polymer Chemistry
- Composite Polymeric Materials
- Polymer Physics
- Applications of Polymers
- Advanced Polymer Structures
- Role of Polymers in biology and biological systems
- Polymer Material Science and Engineering
The Keynote presentations were given by:
- Title: Inorganic/organic hybridized polymers for use in various high performance applications
David Michael Parish, Sherwin Williams Company, USA
- Title: Use of combination crp-thermal cure in free radical bulk polymerization systems
Michael O Wells, Reynolds Polymer Technology, USA
- Title: Mechanical and thermal properties of polyethylene modified with different natural fillers
Janusz Wojciech Sikora, Lublin University of Technology, Poland
- Title: Droplet microfluidic platform technologies for polymer synthesis applications
Carolyn L Ren, University of Waterloo, Canada
With the grand success of Polymer Chemistry 2019, we are glad to announce our next upcoming conference “4th World Congress on Polymer Chemistry” which is going to be held in Vienna, Austria during October 26-27, 2020.
Bookmark your dates…Hoping to meet you again coming year at Vienna!!!
Conference Highlights
- Biopolymers and Biomaterials
- Recycling and waste management of Biopolymers
- Future Scope of Biopolymers and Polymers
- 3D Printing Polymers
- Applications of Biopolymers and Polymer Chemistry
- Polymer Nanotechnology
- Polymer Physics and its Characteristics
- Biopolymers in Tissue Engineering
- Synthetic and Natural Polymers
- Polymer -Optics, Fibre and Lasers
- Organics Polymers
- Biopolymers from Renewable Sources
- Bio-plastics and Bioinformatics
- Recent advancements in Biopolymers and Polymer Chemistry
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | October 26-27, 2020 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by